Basel III: International Regulatory Framework for Banks
October 27, 2020
Happy to announce new partnership with Sumsub
November 5, 2020Risk definition
- Possibility that an outcome or investment’s actual gains will differ from an expected outcome or return.
- Includes the possibility of losing some or all of an original investment.
- It measures the uncertainty that an investor is willing to take to realize a gain
Risk management is the process of identifying, assessing and controlling threats to an organization’s capital and earnings. These threats, or risks, could stem from a wide variety of sources, including financial uncertainty, legal liabilities, strategic management errors, accidents and natural disasters. IT security threats and data-related risks, and the risk management strategies to alleviate them, have become a top priority for digitized companies. As a result, a risk management plan increasingly includes companies’ processes for identifying and controlling threats to its digital assets, including proprietary corporate data, a customer’s personally identifiable information (PII) and intellectual property.
Risk vs. Reward
Broker-dealers, like all businesses, live in a world of risk – operational risk, legal risk, reputation risk, managerial risk, credit risk, among others. Of course, the overarching concern – regulatory risk – is something unique to regulated entities. In many respects, management of any type of risk comes down to the same calculus faced by a broker-dealer’s customers, that is, the ability to balance risk against the potential rewards. Both in theory, and typically in practice, investors make investments hoping the potential reward – profits – outweighs the risks attendant to their particular investments.
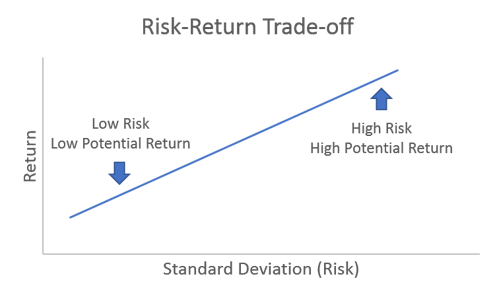
Risk return tradeoff is the balance between the desire for lowest possible risk and highest possible return.
- This is only a theoretical approach – high risk does not necessarily mean high return.
- Consider expected return and volatility compared to the rate of return
Sources of risk in the Brokerage Business:
- Internal (failing to gain expected market share, compliance risks, credit risks)
- Competition risks (banks, other security traders, copied innovations, constraints on innovation)
- Loss of a favorable business environment (macroeconomic changes)
Management of customer risk
An accurate customer risk assessment will help you acquire the most profitable consumers while minimizing risk.
Management of customer risk includes:
- Establishing margin requirements and position limits at adequate levels
- Reviewing significant market exposures at least daily
- Calling for additional collateral modifying margin requirements or position limits, reducing position size
- Identifying and protecting customer property in their custody
- Identifying cheating and arbitrage trading
Download our Presentation below to find out more about:
- Risk Profile
- Financial Risk – types and evaluation
- Tools and measures to control financial risk
- Risk for Brokerage Firms – market and customers