Smart prop trading is no longer a specialized idea only used by a small number of highly developed companies. In a setting where long-term success is determined by capital efficiency, payout consistency, and regulatory-style discipline, it has become an essential evolution. Conventional prop trading models, which mainly depend on trader discretion and lax controls, are difficult to scale and frequently fail when risk is not controlled.
Related articles:
- Top 10 Forex CRM Best Features Every Broker Needs
- Prop Trading Solutions: Key Features and Top Provider
This article explains how automation, behavioral controls, and structured rules in smart prop trading allow for cleaner risk management, transforming risk from a liability into a strategic advantage.
What Smart Prop Trading Really Means?
The best way to conceptualize smart prop trading is as a system-first strategy for proprietary trading. It puts capital preservation, data-driven decision-making, and rule enforcement ahead of chasing short-term profits.
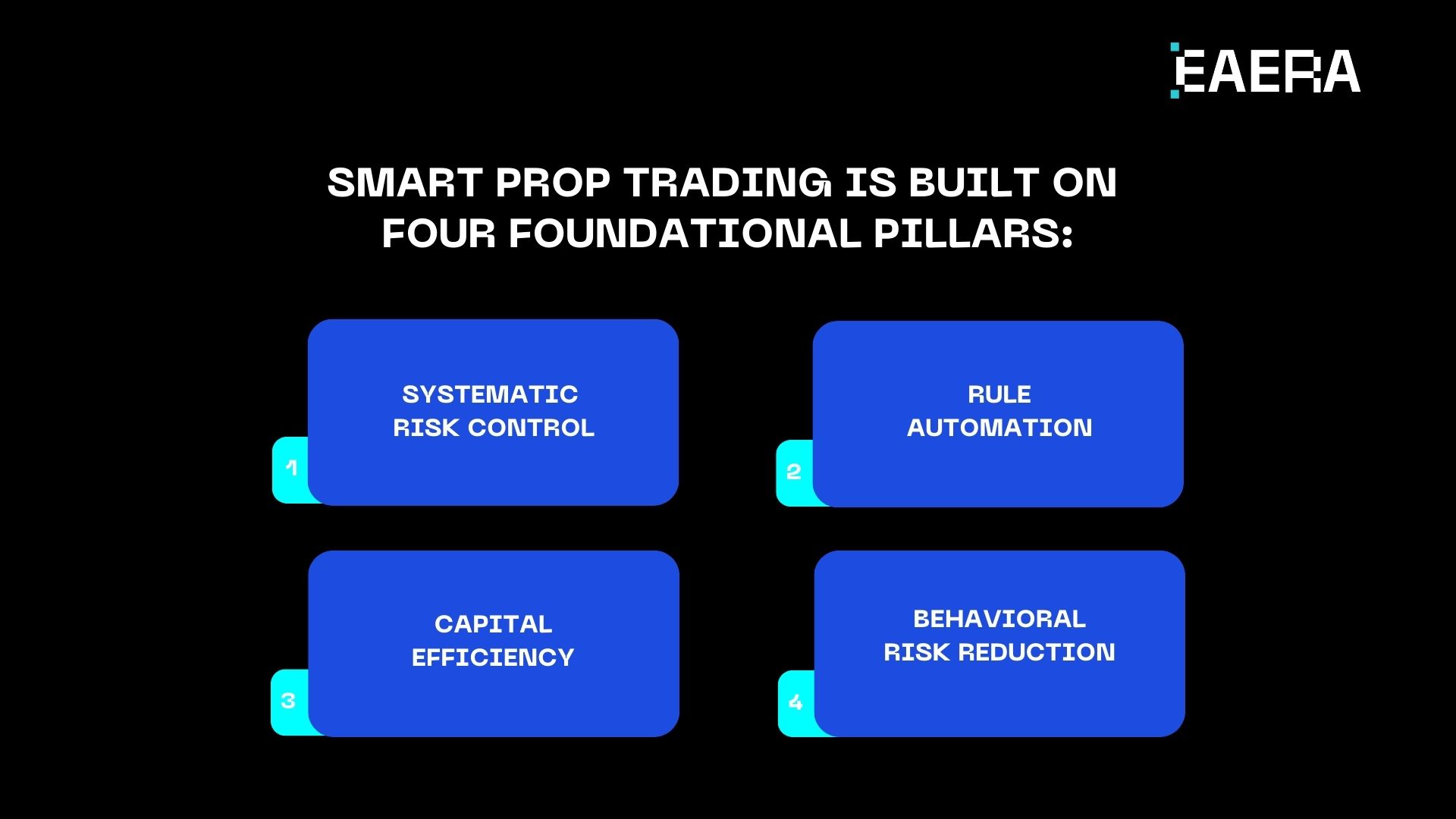
At its core, smart prop trading is built on four foundational pillars:
1. Systematic risk control
Each trade eliminates uncertainty and emotional decision-making by operating within predetermined risk boundaries.
2. Rule automation
Because systems, not people, enforce risk regulations, bias and inconsistency are eliminated.
3. Capital efficiency
Traders who show consistent performance—rather than sporadic victories—are given capital in a dynamic manner.
4. Behavioral risk reduction
Trader psychology is actively managed and regarded as a risk variable.
Smart prop trading is predicated on the idea that discipline must be engineered rather than hoped for, in contrast to traditional discretionary prop trading, where traders are trusted to self-regulate. It goes beyond retail-style prop models by incorporating performance analytics, adaptive thresholds, and real-time monitoring.
To put it briefly, design-based risk management takes the place of trust-based risk management in smart prop trading.
Why Risk Management Is the Real Edge in Prop Trading?
Profits are evident in prop trading, but survival is determined by risk. Most prop firm failures are caused by uncontrolled exposure and uneven enforcement rather than a lack of profitable traders.
Typical risk breakdowns consist of:
- Using excessive leverage when on winning streaks
- Positions that are correlated among traders
- Trading revenge following drawdowns
- Ignoring shifts in the volatility regime
Risk management is reframed by smart prop trading as a competitive advantage rather than limitation. Predictable payouts outperform sporadic windfalls, which is a fundamental truth understood by businesses that thrive and grow.
When risk is strictly managed:
- Drawdowns are shallow and recoverable
- Payout cycles become stable
- Accurate capital forecasting
- Trader attrition declines
For this reason, smart prop trading concentrates more on precisely containing downside than on maximizing upside.
Core Smart Prop Trading Tactics for Cleaner Risk Control
This is the point at which theory becomes practice. The operational foundation of smart prop trading consists of the following strategies.
1. Dynamic Position Sizing
The size of a position is no longer fixed.
- Exposure is adjusted by equity-based sizing when the account balance shifts.
- During times of high volatility, volatility adjusted sizing lowers risk.
- Risk-per-trade limits guarantee that losses stay proportionate.
This strategy keeps traders from inadvertently increasing risk when things are volatile.
2. Drawdown-First Rule Design
Smart prop trading begins with drawdown logic rather than profit targets.
- Daily drawdown limits prevent emotional spirals
- Maximum drawdown thresholds protect firm capital
- Trailing drawdown models adapt to account growth
Profitability is a natural byproduct of creating regulations around loss of containment.
3. Trade Frequency Governance
One of the most underappreciated risks is overtrading.
- Maximum trades per day limits exposure
- Cooldown periods after losses reduce impulsive behavior
- Time-based restrictions enforce discipline
Smart prop trading treats excessive activity as a risk signal, not productivity.
4. Session and News Filters
Market conditions matter.
- Trading session controls limit exposure to low-liquidity periods
- High-impact news filters prevent volatility-driven breaches
- Instrument-specific rules account for asset behavior
By using these filters, traders can only work in settings that fit their strategy profile.

Automation and Data: Turning Rules into Enforced Discipline
Risk enforcement by hand is not scalable. Automation is the first line of defense for smart prop trading.
Risk engines that operate automatically:
- Track exposure in real time
- Instantaneously lock accounts in the event of a breach
- Apply the same regulations to all traders.
Enforcement is then transformed into insight by data. Important metrics consist of:
- Risk-to-reward stability
- Frequency of rule violations
- Drawdown recovery time
- Breach clustering patterns
Automation, analytics, and governance can all be combined into a single risk framework, as shown by enterprise-grade platforms like EAERA. Predictability at scale is the objective, not surveillance.
A rule is not a rule in smart prop trading if it can be circumvented. Automation guarantees complete discipline.
Trader Behavior Management as a Risk Layer
There are other sources of risk besides markets. Behavioral volatility is specifically addressed by smart prop trading.
Important psychological risks consist of:
- Overconfidence following winning runs
- An increase in risk due to loss aversion
- Decision errors caused by fatigue
Smart controls use design to reduce these risks:
- Following drawdowns, automatic cooldowns
- After infractions, temporary trading locks
- Progressive capital scaling tied to consistency, not profit size
Smart prop trading lowers discretionary errors without restricting trader potential by incorporating these mechanisms. Instead of being optional, discipline becomes structural.
Building a Scalable Smart Prop Trading Framework
Systems, incentives, and philosophy must all be in sync for scalability. Usually, a smart prop trading framework takes the following actions:
- Define a risk philosophy
Capital preservation and consistency come first. - Translate philosophy into enforceable rules
Ambiguous guidelines are replaced with binary logic. - Automate enforcement
Systems execute rules without exception. - Monitor and iterate
Data is used to refine thresholds and detect new risk patterns. - Align incentives with risk KPIs
Traders are rewarded for stability, not volatility.
The coexistence of risk management, trader experience, and operational governance within a single ecosystem is demonstrated by infrastructure providers such as EAERA. The result is controlled growth rather than more stringent control.
The goal of smart prop trading is to eliminate uncertainty from risk, not to restrict traders. Stable capital allocation, scalable firm economics, and predictable payouts are the results of improved risk management. Businesses that incorporate discipline into their systems will perform better than those that rely on discretion in an increasingly competitive prop trading environment.
The operating system for long-term resilience, institutional credibility, and repeatable performance across changing market conditions is smart prop trading, which is no longer optional.












